For most Americans the 1990s would be a time of peace, prosperity, and rapid technological change. Some attributed this to the "Reagan Revolution" and the end of the Cold War, others to the return of a Democrat to the presidency. During this period the majority of Americans - political affiliation aside - asserted their support for traditional family values, often grounded in their faiths. New York Times columnist David Brooks suggested that the country was experiencing "moral self-repair," as "many of the indicators of social breakdown, which shot upward in the late 1960s and 1970s, and which plateaued at high levels in the 1980s," were now in decline.
Improved crime and other social statistics aside, American politics remained ideological, emotional, and characterized by intense divisions. Shortly after the nation entered the new millennium, moreover, its post-Cold War sense of security was jolted by an unprecedented terrorist attack that launched it on a new and difficult international track.
1992 Presidential Election
As the 1992 presidential election approached, Americans found themselves in a world transformed in ways almost unimaginable four years earlier. The familiar landmarks of the Cold War - from the Berlin Wall to intercontinental missiles and bombers on constant high alert - were gone. Eastern Europe was independent, the Soviet Union had dissolved, Germany was united, Arabs and Israelis were engaged in direct negotiations, and the threat of nuclear conflict was greatly diminished. It was as though one great history volume had closed and another had opened.
Yet at home, Americans were less sanguine, and they faced some deep and familiar problems. The United States found itself in its deepest recession since the early 1980s. Many of the job losses were occurring among white-collar workers in middle management positions, not solely, as earlier, among blue-collar workers in the manufacturing sector. Even when the economy began recovering in 1992, its growth was virtually imperceptible until late in the year. Moreover, the federal deficit continued to mount, propelled most strikingly by rising expenditures for health care.
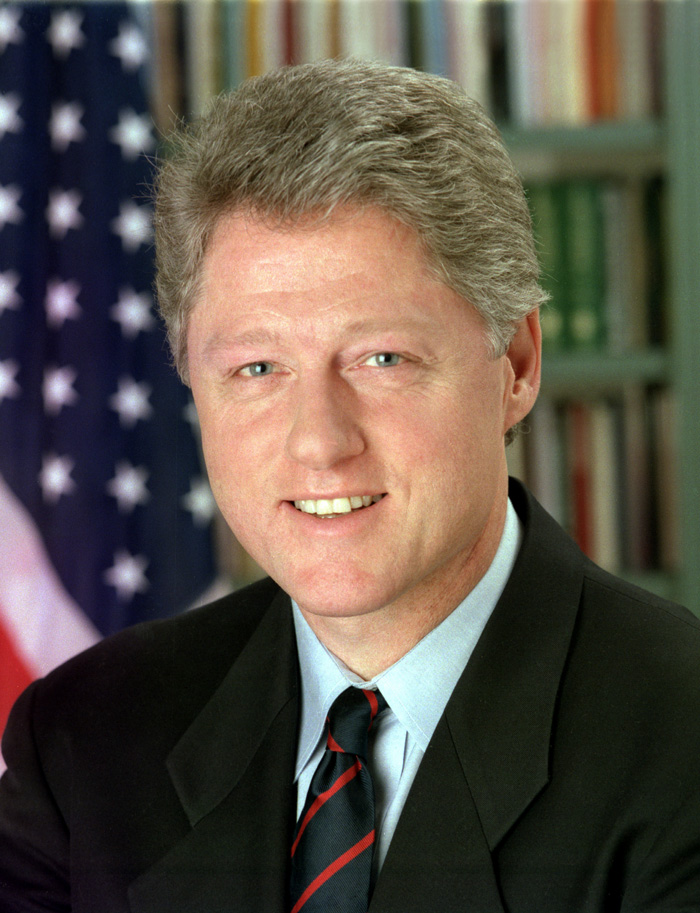
President George Bush and Vice President Dan Quayle easily won renomination by the Republican Party. On the Democratic side, Bill Clinton, governor of Arkansas, defeated a crowded field of candidates to win his party's nomination. As his vice presidential nominee, he selected Senator Al Gore of Tennessee, generally acknowledged as one of the Congress's strongest advocates of environmental protection.
The country's deep unease over the direction of the economy also sparked the emergence of a remarkable independent candidate, wealthy Texas entrepreneur H. Ross Perot. Perot tapped into a deep wellspring of frustration over the inability of Washington to deal effectively with economic issues, principally the federal deficit. He possessed a colorful personality and a gift for the telling one-line political quip. He would be the most successful third-party candidate since Theodore Roosevelt in 1912.
The Bush re-election effort was built around a set of ideas traditionally used by incumbents: experience and trust. George Bush, 68, the last of a line of presidents who had served in World War II, faced a young challenger in Bill Clinton who, at age 46, had never served in the military and had participated in protests against the Vietnam War. In emphasizing his experience as president and commander-in-chief, Bush drew attention to Clinton's inexperience at the national level.
Bill Clinton organized his campaign around another of the oldest and most powerful themes in electoral politics: youth and change. As a high-school student, Clinton had once met President Kennedy; 30 years later, much of his rhetoric consciously echoed that of Kennedy in his 1960 campaign.
As governor of Arkansas for 12 years, Clinton could point to his experience in wrestling with the very issues of economic growth, education, and health care that were, according to public opinion polls, among President Bush's chief vulnerabilities. Where Bush offered an economic program based on lower taxes and cuts in government spending, Clinton proposed higher taxes on the wealthy and increased spending on investments in education, transportation, and communications that, he believed, would boost the nation's productivity and growth and thereby lower the deficit. Similarly, Clinton's health care proposals called for much heavier involvement by the federal government than Bush's.
Clinton proved to be a highly effective communicator, not least on television, a medium that highlighted his charm and intelligence. The incumbent's very success in handling the end of the Cold War and reversing the Iraqi thrust into Kuwait lent strength to Clinton's implicit argument that foreign affairs had become relatively less important, given pressing social and economic needs at home.
On November 3, Bill Clinton won election as the 42nd president of the United States, receiving 43 percent of the popular vote against 37 percent for Bush and 19 percent for Perot.
A New Presidency
Clinton was in many respects the perfect leader for a party divided between liberal and moderate wings. He tried to assume the image of a pragmatic centrist who could moderate the demands of various Democratic Party interest groups without alienating them.
Avoiding ideological rhetoric that declared big government to be a positive good, he proposed a number of programs that earned him the label "New Democrat." Control of the federal bureaucracy and judicial appointments provided one means of satisfying political claims of organized labor and civil rights groups. On the ever-controversial abortion issue, Clinton supported the Roe v. Wade decision, but also declared that abortion should be "safe, legal, and rare."
President Clinton's closest collaborator was his wife, Hillary Rodham Clinton. In the campaign, he had quipped that those who voted for him "got two for the price of one." She supported her husband against accusations about his personal life.
As energetic and as activist as her husband, Ms. Clinton assumed a more prominent role in the administration than any first lady before her, even Eleanor Roosevelt. Her first important assignment would be to develop a national health program. In 2000, with her husband's administration coming to a close, she would be elected a U.S. senator from New York.
Launching a New Domestic Policy
In practice, Clinton's centrism demanded choices that sometimes elicited vehement emotions. The president's first policy initiative was designed to meet the demands of gays, who, claiming a group status as victims of discrimination, had become an important Democratic constituency.
Immediately after his inauguration, President Clinton issued an executive order rescinding the long-established military policy of dismissing known gays from the service. The order quickly drew furious criticism from the military, most Republicans, and large segments of American society. Clinton quickly modified it with a "don't ask, don't tell" order that effectively restored the old policy but discouraged active investigation of one's sexual practices.
The effort to achieve a national health plan proved to be a far larger setback. The administration set up a large task force, chaired by Hillary Clinton. Composed of prominent policy intellectuals and political activists, it labored in secrecy for months to develop a plan that would provide medical coverage for every American.
The working assumption behind the plan was that a government-managed "single-payer" plan could deliver health services to the entire nation more efficiently than the current decentralized system with its thousands of insurers and disconnected providers. As finally delivered to Congress in September 1993, however, the plan mirrored the complexity of its subject. Most Republicans and some Democrats criticized it as a hopelessly elaborate federal takeover of American medicine. After a year of discussion, it died without a vote in Congress.
Clinton was more successful on another matter with great repercussions for the domestic economy. The previous president, George Bush, had negotiated the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) to establish fully open trade between Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Key Democratic constituencies opposed the agreement. Labor unions believed it would encourage the export of jobs and undermine American labor standards. Environmentalists asserted that it would lead American industries to relocate to countries with weak pollution controls. These were the first indications of a growing movement on the left wing of American politics against the vision of an integrated world economic system.
President Clinton nonetheless accepted the argument that open trade was ultimately beneficial to all parties because it would lead to a greater flow of more efficiently produced goods and services. His administration not only submitted NAFTA to the Senate, it also backed the establishment of a greatly liberalized international trading system to be administered by the World Trade Organization (WTO). After a vigorous debate, Congress approved NAFTA in 1993. It would approve membership in the WTO a year later.
Although Clinton had talked about a "middle class tax cut" during the presidential campaign, he submitted to Congress a budget calling for a general tax increase. It originally included a wide tax on energy consumption designed to promote conservation, but that was quickly replaced by a nominal increase in the federal gasoline tax. It also taxed social security benefits for recipients of moderate income and above. The big emphasis, however, was on increasing the income tax for high earners. The subsequent debate amounted to a rerun of the arguments between tax cutters and advocates of "fiscal responsibility" that had marked the Reagan years. In the end, Clinton got his way, but very narrowly. The tax bill passed the House of Representatives by only one vote.
By then, the congressional election campaigns of 1994 were under way. Although the administration already had made numerous foreign policy decisions, issues at home were clearly most important to the voters. The Republicans depicted Clinton and the Democrats as unreformed tax and spenders. Clinton himself was already beleaguered with charges of past financial impropriety in an Arkansas real estate project and new claims of sexual impropriety. In November, the voters gave the Republicans control of both houses of Congress for the first time since the election of 1952. Many observers believed that Bill Clinton would likely be a one-term president. Apparently making a decision to conform to new political realities, Clinton instead moderated his political course. Policy initiatives for the remainder of his presidency were few. Contrary to Republican predictions of doom, the tax increases of 1993 did not get in the way of a steadily improving economy.
The new Republican leadership in the House of Representatives, by contrast, pressed hard to achieve its policy objectives, a sharp contrast with the administration's new moderate tone. When right-wing extremists bombed an Oklahoma City federal building in April 1995, Clinton responded with a tone of moderation and healing that heightened his stature and implicitly left some doubts about his conservative opponents. At the end of the year, he vetoed a Republican budget bill, shutting down the government for weeks. Most of the public seemed to blame the Republicans.
The president also co-opted part of the Republican program. In his State of the Union address of January 1996, he ostentatiously declared, "The era of big government is over." That summer, on the eve of the presidential campaign, he signed a major welfare reform bill that was essentially a Republican product. Designed to end permanent support for most welfare recipients and move them to work, it was opposed by many in his own party. By and large, it would prove successful in operation over the next decade.
The American economy in the 1990s
By the mid-1990s, the country had not simply recovered from the brief, but sharp, recession of the Bush presidency. It was entering an era of booming prosperity, and doing so despite the decline of its traditional industrial base. Probably the major force behind this new growth was the blossoming of the personal computer (PC).
Less than 20 years after its introduction, the PC had become a familiar item, not simply in business offices of all types, but in homes throughout America. Vastly more powerful than anyone could have imagined two decades earlier, able to store enormous amounts of data, available at the cost of a good refrigerator, it became a common appliance in American homes.
Employing prepackaged software, people used it for bookkeeping, word processing, or as a depository for music, photos, and video. The rise of the Internet, which grew out of a previously closed defense data network, provided access to information of all sorts, created new shopping opportunities, and established e-mail as a common mode of communication. The popularity of the mobile phone created a huge new industry that cross-fertilized with the PC.
Instant communication and lightning-fast data manipulation speeded up the tempo of many businesses, greatly enhancing productivity and creating new opportunities for profit. Fledgling industries that fed demand for the new equipment became multi-billion-dollar companies almost overnight, creating an enormous new middle class of software technicians, managers, and publicists.
A final impetus was the turn of the millennium. A huge push to upgrade outdated computing equipment that might not recognize the year 2000 brought data technology spending to a peak.
These developments began to take shape during Clinton's first term. By the end of his second one they were fueling a surging economy. When he had been elected president, unemployment was at 7.4 percent. When he stood for re-election in 1996, it was at 5.4 percent. When voters went to the polls to choose his successor in November 2000, it was 3.9 percent. In many places, the issue was less one of taking care of the jobless than of finding employable workers.
No less a figure than Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan viewed a rapidly escalating stock market with concern and warned of "irrational exuberance." Investor exuberance, at its greatest since the 1920s, continued in the conviction that ordinary standards of valuation had been rendered obsolete by a "new economy" with unlimited potential. The good times were rolling dangerously fast, but most Americans were more inclined to enjoy the ride while it lasted than to plan for a coming bust.
The Election of 1996 and the Political Aftermath
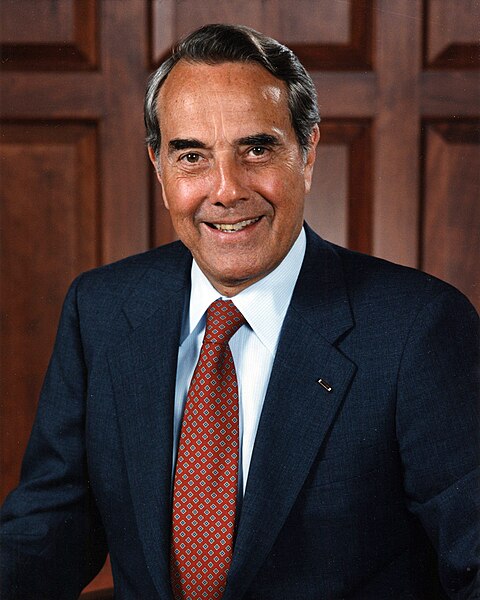
President Clinton undertook his campaign for re-election in 1996 under the most favorable of circumstances. If not an imposing personality in the manner of a Roosevelt, he was a natural campaigner, whom many felt had an infectious charm. He presided over a growing economic recovery. He had positioned himself on the political spectrum in a way that made him appear a man of the center leaning left. His Republican opponent, Senator Robert Dole of Kansas, Republican leader in the upper house, was a formidable legislator but less successful as a presidential candidate.
Clinton, promising to "build a bridge to the 21st century," easily defeated Dole in a three-party race, 49.2 percent to 40.7 percent, with 8.4 percent to Ross Perot. He thus became the second American president to win two consecutive elections with less than a majority of the total vote. (The other was Woodrow Wilson in 1912 and 1916.) The Republicans, however, retained control of both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
Clinton never stated much of a domestic program for his second term. The highlight of its first year was an accord with Congress designed to balance the budget, further reinforcing the president's standing as a fiscally responsible moderate liberal.
In 1998, American politics entered a period of turmoil with the revelation that Clinton had carried on an affair inside the White House with a young intern. At first the president denied this, telling the American people: "I did not have sexual relations with that woman." The president had faced similar charges in the past. In a sexual harassment lawsuit filed by a woman he had known in Arkansas, Clinton denied under oath the White House affair. This fit most Americans' definition of perjury. In October 1998, the House of Representatives began impeachment hearings, focusing on charges of perjury and obstruction of justice.
Whatever the merits of that approach, a majority of Americans seemed to view the matter as a private one to be sorted out with one's family, a significant shift in public attitude. Also significantly, Hillary Clinton continued to support her husband. It surely helped also that the times were good. In the midst of the House impeachment debate, the president announced the largest budget surplus in 30 years. Public opinion polls showed Clinton's approval rating to be the highest of his six years in office.
That November, the Republicans took further losses in the midterm congressional elections, cutting their majorities to razor-thin margins. House Speaker Newt Gingrich resigned, and the party attempted to develop a less strident image. Nevertheless, in December the House voted the first impeachment resolution against a sitting president since Andrew Johnson (1868), thereby handing the case to the Senate for a trial.
Clinton's impeachment trial, presided over by the Chief Justice of the United States, held little suspense. In the midst of it, the president delivered his annual State of the Union address to Congress. He never testified, and no serious observer expected that any of the several charges against him would win the two-thirds vote required for removal from office. In the end, none got even a simple majority. On February 12, 1999, Clinton was acquitted of all charges.
American Foreign Relations in the Clinton Years
Bill Clinton did not expect to be a president who emphasized foreign policy. However, like his immediate predecessors, he quickly discovered that all international crises seemed to take a road that led through Washington.
He had to deal with the messy aftermath of the 1991 Gulf War. Having failed to depose Saddam Hussein, the United States, backed by Britain, attempted to contain him. A United Nations-administered economic sanctions regime, designed to allow Iraq to sell enough oil to meet humanitarian needs, proved relatively ineffective. Saddam funneled much of the proceeds to himself, leaving large masses of his people in misery. Military "no-fly zones," imposed to prevent the Iraqi government from deploying its air power against rebellious Kurds in the north and Shiites in the south, required constant U.S. and British air patrols, which regularly fended off anti-aircraft missiles.
The United States also provided the main backing for U.N. weapons inspection teams, whose mission was to ferret out Iraq's chemical, biological, and nuclear programs, verify the destruction of existing weapons of mass destruction, and suppress ongoing programs to manufacture them. Increasingly obstructed, the U.N. inspectors were finally expelled in 1998. On this, as well as earlier occasions of provocation, the United States responded with limited missile strikes. Saddam, Secretary of State Madeline Albright declared, was still "in his box."
The seemingly endless Israeli-Palestinian dispute inevitably engaged the administration, although neither President Clinton nor former President Bush had much to do with the Oslo agreement of 1993, which established a Palestinian "authority" to govern the Palestinian population within the West Bank and the Gaza Strip and obtained Palestinian recognition of Israel's right to exist.
As with so many past Middle Eastern agreements in principle, however, Oslo eventually fell apart when details were discussed. Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat rejected final offers from Israeli leader Ehud Barak in 2000 and January 2001. A full-scale Palestinian insurgency, marked by the use of suicide bombers, erupted. Barak fell from power, to be replaced by the far tougher Ariel Sharon. U.S. identification with Israel was considered by some a major problem in dealing with other issues in the region, but American diplomats could do little more than hope to contain the violence. After Arafat's death in late 2004, new Palestinian leadership appeared more receptive to a peace agreement, and American policy makers resumed efforts to promote a settlement.
President Clinton also became closely engaged with "the troubles" in Northern Ireland. On one side was the violent Irish Republican Army, supported primarily by those Catholic Irish who wanted to incorporate these British counties into the Republic of Ireland. On the other side were Unionists, with equally violent paramilitary forces, supported by most of the Protestant Scots-Irish population, who wanted to remain in the United Kingdom.
Clinton gave the separatists greater recognition than they ever had obtained in the United States, but also worked closely with the British governments of John Major and Tony Blair. The ultimate result, the Good Friday peace accords of 1998, established a political process but left many details to be worked out. Over the next several years, peace and order held better in Northern Ireland than in the Middle East, but remained precarious. The final accord continued to elude negotiators. The post-Cold War disintegration of Yugoslavia - a state ethnically and religiously divided among Serbs, Croats, Slovenes, Bosnian Muslims, and Albanian Kosovars - also made its way to Washington after European governments failed to impose order. The Bush administration had refused to get involved in the initial violence; the Clinton administration finally did so with great reluctance after being urged to do so by the European allies. In 1995, it negotiated an accord in Dayton, Ohio, to establish a semblance of peace in Bosnia. In 1999, faced with Serbian massacres of Kosovars, it led a three-month NATO bombing campaign against Serbia, which finally forced a settlement.
In 1994, the administration restored ousted President Jean-Bertrand Aristide to power in Haiti, where he would rule for nine years before being ousted again. The intervention was largely a result of Aristide's carefully cultivated support in the United States and American fears of waves of Haitian illegal immigrants.
In sum, the Clinton administration remained primarily inward looking, willing to tackle international problems that could not be avoided and, in other instances, forced by the rest of the world to do so.