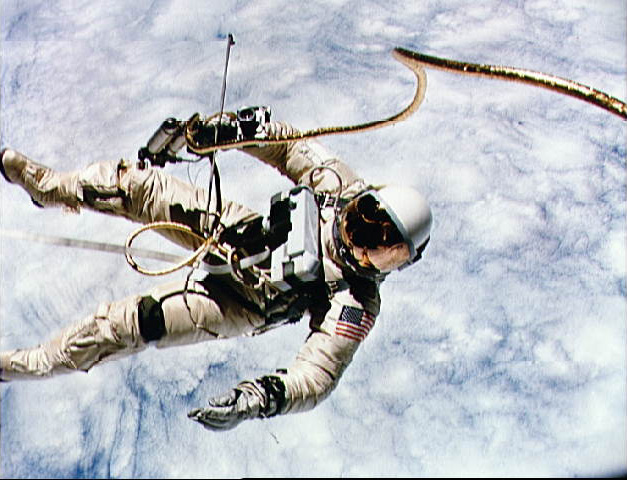
On May 25, 1961, President John F. Kennedy spoke before a special joint session of Congress and challenged the country to safely send and return an American to the Moon before the end of the decade. President Kennedy's vision for the three-year old National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) motivated the United States to develop enormous technological capabilities and inspired the nation to reach new heights.
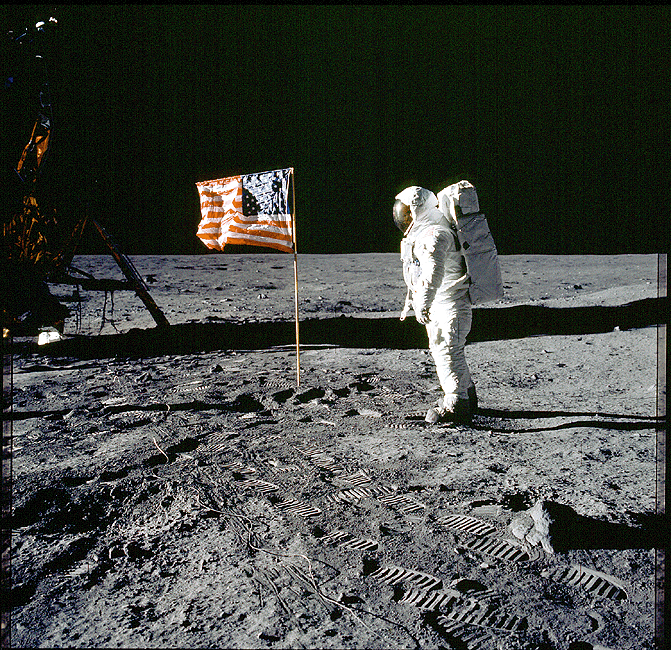
Eight years after Kennedy's speech, NASA's Apollo program successfully met the president's challenge. On July 20, 1969, the world witnessed one of the most astounding technological achievements in the 20th century. Neil Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin became the first humans to set foot on the Moon, while Mike Collins orbited the Moon in the Command Module. Armstrong's words, "That's one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind," were heard around the world and inspired a generation. This amazing accomplishment required the collaboration of hundreds of thousands of determined individuals and the committed resources of our nation.
The "race to space" was initiated on October 4, 1957 with the successful launch by the Soviet Union of Sputnik I. Sputnik, the world's first artificial satellite, measured the size of a beach ball (58 cm or 22.8 inches in diameter), weighed only 83.6 kg (183.9 lbs), and orbited the Earth in 98 minutes on an elliptical path. Although relatively small in size, its impact was huge. Americans did not want to be left in the dust by the Soviet's technological advances.
This was at the height of the Cold War and America also worried that the Soviets would use this technology for military purposes. Concerns over Soviet capabilities to launch nuclear weapons quickly emerged and heightened fears among Americans. Despite being economically overshadowed by the United States, the Soviet Union continued its ominous presence in the arms race and space race.
A newly organized NASA met challenges along the way as they strived to meet the goal set by President Kennedy. Despite a rough start to catch the Soviet Union, the United States became the first country to conduct a manned lunar orbit in December of 1968 (Apollo 8). This was followed by the first lunar landing on July 20, 1969 (Apollo 11). The United States celebrated this victory as Kennedy's vision and the hope of a nation was fulfilled.
Timeline: Americans in space, 1961-1972
1961
-
5 May 1961 -- Earth Suborbital (Shepard)
-
21 July 1961 -- Earth Suborbital (Grissom)
1962
-
20 February 1962 -- Earth Orbiter (Glenn)
-
24 May 1962 -- Earth Orbiter (Carpenter)
-
3 October 1962 -- Earth Orbiter (Schirra)
1963
-
15 May 1963 -- Earth Orbiter (Cooper)
1965
-
23 March 1965 -- Earth Orbiter (Grissom, Young)
-
3 June 1965 -- Earth Orbiter (McDivitt, White)
-
21 August 1965 -- Earth Orbiter (Cooper, Conrad)
-
4 December 1965 -- Earth Orbiter (Borman, Lovell)
-
15 December 1965 -- Earth Orbiter (Schirra, Stafford)
1966
-
16 March 1966 -- Earth Orbiter (Armstrong, Scott)
-
3 June 1966 -- Earth Orbiter (Stafford, Cernan)
-
18 July 1966 -- Earth Orbiter (Young, Collins)
-
12 September 1966 -- Earth Orbiter (Conrad, Gordon)
-
11 November 1966 -- Earth Orbiter (Lovell, Aldrin)
1968
-
11 October 1968 -- Earth Orbiter (Schirra, Eisele, Cunningham)
-
21 December 1968 -- Lunar Orbiter (Borman, Lovell, Anders)
1969
-
3 March 1969 -- Earth Orbiter (McDivitt, Scott, Schweikart)
-
18 May 1969 -- Lunar Orbiter (Stafford, Young, Cernan)
-
16 July 1969 -- Lunar Landing (Armstrong, Aldrin, Collins)
-
14 November 1969 -- Lunar Landing (Conrad, Bean, Gordon)
1970
-
11 April 1970 -- Lunar Mission - Landing Aborted (Lovell, Haise, Swigert)
1971
-
31 January 1971 -- Lunar Landing (Shepard, Mitchell, Roosa)
-
26 July 1971 -- Lunar Landing (Scott, Irwin, Worden)