During the 1850s, the issue of slavery severed the political bonds that had held the United States together. It ate away at the country's two great political parties, the Whigs and the Democrats, destroying the first and irrevocably dividing the second. It produced weak presidents whose irresolution mirrored that of their parties. It eventually discredited even the Supreme Court.
The moral fervor of abolitionist feeling grew steadily. In 1852, Harriet Beecher Stowe published Uncle Tom's Cabin, a novel provoked by the passage of the Fugitive Slave Law. More than 300,000 copies were sold the first year. Presses ran day and night to keep up with the demand. Although sentimental and full of stereotypes, Uncle Tom's Cabin portrayed with undeniable force the cruelty of slavery and posited a fundamental conflict between free and enslaving societies. It inspired widespread enthusiasm for the antislavery cause, appealing as it did to basic human emotions -indignation at injustice and pity for the helpless individuals exposed to ruthless exploitation.
In 1854 the issue of slavery in the territories was renewed and the quarrel became more bitter. The region that now comprises Kansas and Nebraska was being rapidly settled, increasing pressure for the establishment of territorial, and eventually, state governments.
Under terms of the Missouri Compromise of 1820, the entire region was closed to slavery. Dominant enslaving elements in Missouri objected to letting Kansas become a free territory, for their state would then have three free-soil neighbors (Illinois, Iowa, and Kansas) and might be forced to become a free state as well. Their congressional delegation, backed by Southerners, blocked all efforts to organize the region.
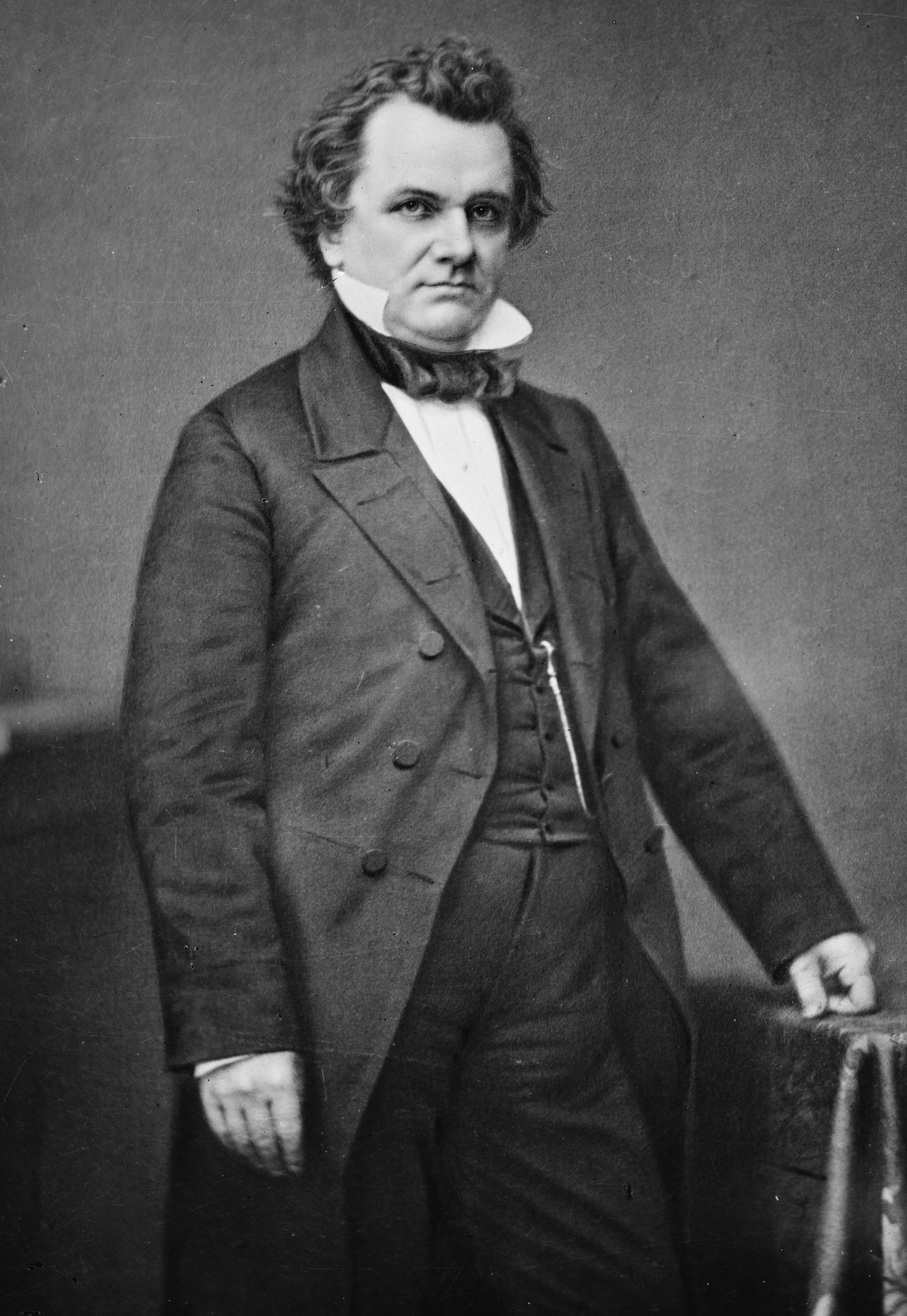
At this point, Stephen A. Douglas enraged all free-soil supporters. Douglas argued that the Compromise of 1850, having left Utah and New Mexico free to resolve the slavery issue for themselves, superseded the Missouri Compromise. His plan called for two territories, Kansas and Nebraska. It permitted settlers to carry enslaved people into them and eventually to determine whether they should enter the Union as free or enslaving states.
Douglas's opponents accused him of currying favor with the South in order to gain the presidency in 1856. The free-soil movement, which had seemed to be in decline, reemerged with greater momentum than ever. Yet in May 1854, Douglas's plan, in the form of the Kansas-Nebraska Act, passed Congress to be signed by President Franklin Pierce. Southern enthusiasts celebrated with cannon fire. But when Douglas subsequently visited Chicago to speak in his own defense, the ships in the harbor lowered their flags to half-mast, the church bells tolled for an hour, and a crowd of 10,000 hooted so loudly that he could not make himself heard.
The immediate results of Douglas's ill-starred measure were momentous. The Whig Party, which had straddled the question of slavery expansion, sank to its death, and in its stead a powerful new organization arose, the Republican Party, whose primary demand was that slavery be excluded from all the territories. In 1856, it nominated John Fremont, whose expeditions into the Far West had won him renown. Fremont lost the election, but the new party swept a great part of the North. Such free-soil leaders as Salmon P. Chase and William Seward exerted greater influence than ever. Along with them appeared a tall, lanky Illinois attorney, Abraham Lincoln.
Meanwhile, the flow of both Southern enslavers and antislavery families into Kansas resulted in armed conflict. Soon the territory was being called "bleeding Kansas." The Supreme Court made things worse with its infamous 1857 Dred Scott decision.
Scott was an enslaved person from Missouri who, some 20 years earlier, had been taken by his enslaver to live in Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory; in both places, slavery was banned. Returning to Missouri and becoming discontented with his life there, Scott sued for liberation on the ground of his residence on free soil. A majority of the Supreme Court - dominated by Southerners - decided that Scott lacked standing in court because he was not a citizen; that the laws of a free state (Illinois) had no effect on his status because he was the resident of an enslaving state (Missouri); and that enslavers had the right to take their "property" anywhere in the federal territories. Thus, Congress could not restrict the expansion of slavery. This last assertion invalidated former compromises on slavery and made new ones impossible to craft.
The Dred Scott decision stirred fierce resentment throughout the North. Never before had the Court been so bitterly condemned. For Southern Democrats, the decision was a great victory, since it gave judicial sanction to their justification of slavery throughout the territories.
Source Citation:
"An Outline of American History," United States Information Agency. https://archive.org/details/OutlineOfUSHistory/page/n137/mode/2up.