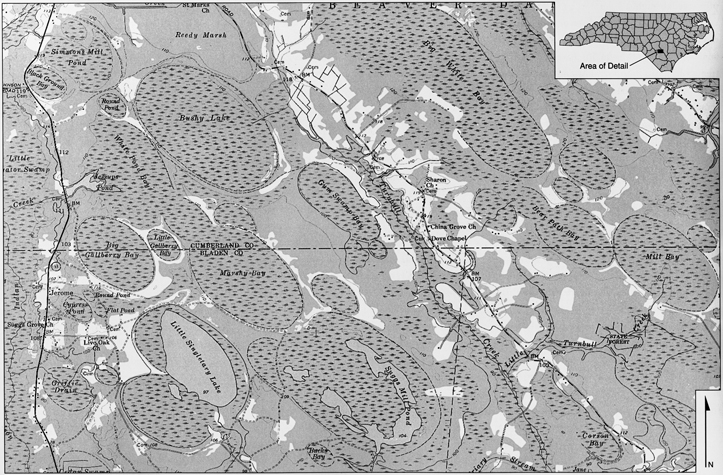
Carolina Bays are oval depressions in the earth's surface concentrated on either side of the North Carolina-South Carolina boundary. They are most numerous in Bladen County, although some are found as far away as Georgia and Maryland. Once thought to number in the hundreds of thousands, there are now fewer than 900 notable Carolina Bays, with about 80 percent of these located in North Carolina. They are oriented in a northwest-southeast direction and frequently have a sand rim on the southeast portion. Varying in size from a few hundred feet to about six miles in length, some of the Carolina Bays, such as those forming Lake Waccamaw, Bay Tree Lake, White Lake, Little Singletary Lake, and Horseshoe Lake, still hold water. Others have become bogs or pocosins of peat or black loam soil or have completely dried up. Lake Waccamaw, the largest, is about 20 feet deep, while White Lake reaches a depth of 15 feet. The depth of the peat in some of the bays that are no longer filled with water measures between 11 and 50 feet.
These unusual formations were first given special attention by geologists in 1895 after L. C. Glenn noticed the shape and other similarities they shared. Popular scientific opinion once held that the bays are the result of a shower or successive showers of meteorites hitting the earth at an angle, although other theories of their origin included ice fragments from a Hudson River basin meteor impact and the tail-fanning of a huge fish. The current formation theory holds that the wave-motion of the receding ocean created pools of standing water that were then elliptically shaped by winds blowing in the same direction for a long period of time.