13 July 1824–15 Mar. 1886

James Iredell Waddell, captain of the Confederate cruiser Shenandoah, was born in Pittsboro, Chatham County, the son of Francis Nash and Elizabeth Davis Moore Waddell. He was the grandson of Alfred Moore and the great-grandson of Hugh Waddell. Reared by his maternal grandmother, Waddell received his early education at the Hillsborough Academy. In 1841 he obtained an acting midshipman's commission in the navy. Shortly after reporting for duty to Norfolk, Va., Waddell challenged another midshipman to a duel and received a serious leg wound that left him with a limp for the rest of his life. In 1846 he served in the Mexican War aboard the Somers in the Gulf of Mexico. Distinguishing himself as a navigator, he was later transferred to Annapolis to take advanced navigation courses.
Between 1850 and 1857 Waddell served on the German-town and Release, patrolling the waters around South America. In 1857 he was again transferred to Annapolis to teach navigation. After visiting Waddell in 1858, Samuel A. Ashe described him as "six feet one inch in height, with a powerful frame weighing more than two hundred pounds." In 1859 Waddell was assigned to duty in the Pacific, where he remained until the Civil War began.
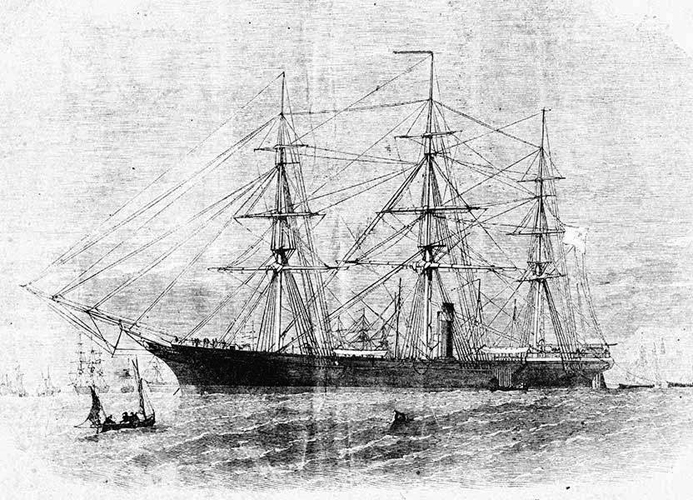
At that time he resigned his commission and went to Richmond to join the Confederacy. On 27 Mar. 1862 he was commissioned a lieutenant in the Confederate navy and after one year of service in the South was ordered to Europe. On 19 Oct. 1864 to took command of the Sea King, a British merchant ship that had been purchased by the Confederacy and refitted as a maritime raider. Rechristened the Shenandoah, it set a course for the Pacific with orders to destroy the New England whaling fleet. The Shenandoah was enormously successful, capturing thirty-eight ships and destroying thirty-two, worth $1,772,223.
The cruise of the Shenandoah, which had been a glorious adventure for Waddell and his crew, ended on a note of tragic irony. On 23 June 1865 they learned from newspaper accounts aboard a captured ship of General Robert E. Lee's surrender at Appomattox the previous April. However, the same dispatches contained Jefferson Davis's Danville proclamation urging the South to fight on. This Waddell and his men proceeded to do. Only in August did they receive definite word that the war was over.

Official Union policy had always considered the Confederate cruisers as pirates. Without a government the Shenandoah was most vulnerable to charges of piracy, and Waddell regarded surrender to the United States as impossible. Deciding that their chances were better in Europe, he set a course by way of Cape Horn for Liverpool, 17,000 miles away. On 6 Nov. 1865 the Shenandoah, the last Confederate cruiser and the only one to sail around the world, reached Liverpool and surrendered to the British government.
Remaining in England until adverse public opinion towards him in the United States subsided, Waddell returned in 1875 and took a position as captain of the San Francisco for the Pacific Mail Company. In 1877, while commanding the San Francisco, he struck an uncharted reef, and the ship sank without losing a passenger. Returning to Annapolis, he took command of a small police force that controlled the oyster fleets in the Chesapeake Bay.
Waddell died of a brain disorder and was buried at St. Anne's Church (Episcopal), Annapolis. He was survived by his wife, the former Ann S. Iglehart of Annapolis, whom he had married in 1848. They had no children. Photographs of Waddell are on file at the North Carolina State Archives, Hillsborough Historical Museum, and North Carolina Collection at the University of North Carolina.