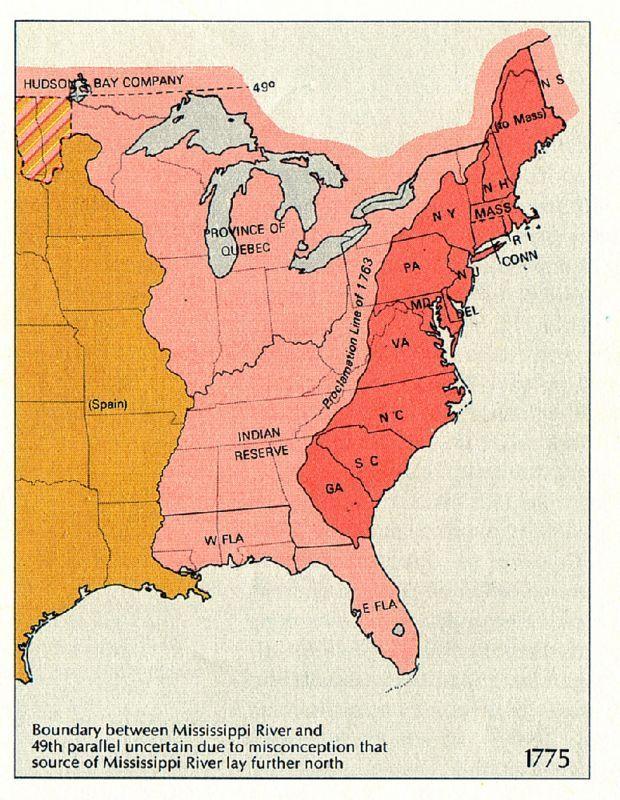
The Proclamation Line of 1763
In the Treaty of Paris (1763) that ended the Seven Years War, Britain gained all of Canada as well as the territory north of New Orleans, Louisiana, and between the Eastern Great Divide and the Mississippi River. France, which was forced to cede this territory, had also ceded the territory west of the Mississippi, known as Louisiana, to Spain in 1762. In the Royal Proclamation of 1763, portions of these new British territories were divided into Quebec and East and West Florida. Most of the territory between the Appalachians and the Mississippi was reserved for American Indians, and colonists were barred from settling west of the "Proclamation Line" that ran down the peak of the Appalachians. This angered many colonists who had fought in the Seven Years' War in hopes that they could gain new land west of the Appalachians. On this map, the territory reserved to the thirteen British North American colonies that would become the United States is shown in red. Other British territory prohibited to these colonies is in pink, and Spanish territory is in orange.
Public Domain
Public Domain is a copyright term that is often used when talking about copyright for creative works. Under U.S. copyright law, individual items that are in the public domain are items that are no longer protected by copyright law. This means that you do not need to request permission to re-use, re-publish or even change a copy of the item. Items enter the public domain under U.S. copyright law for a number of reasons: the original copyright may have expired; the item was created by the U.S. Federal Government or other governmental entity that views the things it creates as in the public domain; the work was never protected by copyright for some other reason related to how it was produced (for example, it was a speech that wasn't written down or recorded); or the work doesn't have enough originality to make it eligible for copyright protection.